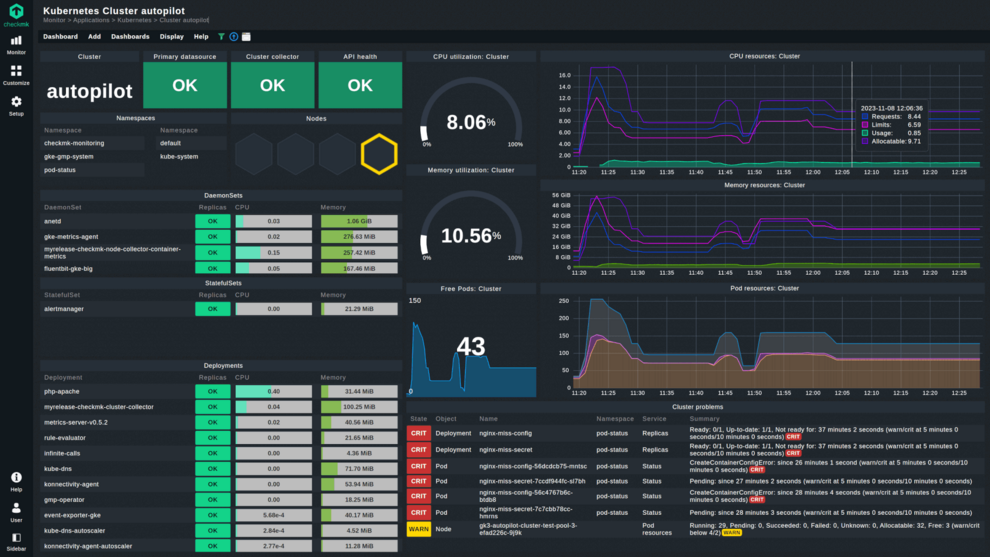
As an Autopilot partner, Checkmk is part of an exclusive group of Google partners that offer privileged partner workloads for GKE Autopilot. This entitles Checkmk to read node-level metrics for GKE Autopilot monitoring.
GKE autopilot vs. standard: What's the difference?
Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) is a Kubernetes container orchestration platform that can run on Google Cloud while providing precise control over cluster management. For development teams that want to minimize the complexity of their Kubernetes environment, Google also offers GKE Autopilot, a serverless, fully managed and automated operating mode of GKE. Instead of manually configuring or managing clusters as with GKE, Google Cloud handles these tasks with GKE Autopilot.
How GKE Autopilot works
GKE Autopilot is an operation mode in which Google Cloud handles cluster management, control plane operations, and complete management of the underlying infrastructure. As a result, user teams no longer need to worry about cluster upgrades, security patches, and operational processes.
In addition, Autopilot clusters are optimized to run most production workloads and provision the appropriate compute resources based on their corresponding Kubernetes manifests. For optimized configuration, Google Cloud follows GKE best practices and recommendations for cluster setup, workloads, scalability, and security.
This means that GKE Autopilot automatically scales the cluster based on workload requirements to ensure that applications have the resources they need. It also aims to avoid over-provisioning by automatically adjusting cluster size to match actual demand, thereby saving costs.
Various security measures, such as automatic patching, cluster isolation, and automatic node remediation, also aim to improve the security of the Kubernetes environment.
Monitoring GKE Autopilot
However, GKE Autopilot's all-inclusive package also comes with certain limitations. It limits the configuration options of the cluster, as it takes away advanced options in order to provide the simplest possible user experience. It also prevents direct access to nodes, as Autopilot manages all nodes.
Because clusters managed by GKE Autopilot typically do not allow workloads that require elevated privileges, monitoring these clusters with a third-party monitoring tool is also more difficult. While monitoring a standard GKE cluster with a Kubernetes monitoring tool is straightforward, Autopilot clusters can only be monitored with privileged access. The exception are Google Cloud partners like Checkmk, who can also monitor GKE Autopilot clusters.
As an Autopilot partner, Checkmk is part of an exclusive group of Google partners that offer privileged partner workloads for GKE Autopilot. Checkmk has gone through an extensive review process with Google and now enjoys elevated privileges, including the ability to read node-level metrics.
This means you can monitor your GKE Autopilot clusters with Checkmk without restrictions, and view all the details of your clusters through the preconfigured and connected dashboards for your Kubernetes monitoring. To learn how to set up Kubernetes monitoring for your GKE Autopilot clusters, read the manual.
Requirements for GKE Autopilot monitoring
Monitoring GKE Autopilot with Checkmk has the following requirements:
- Cluster Collector 1.5.1+
- GKE Autopilot 1.27+
In addition, var_run must be set to readOnly in the YAML file values.yaml to be able to retrieve the corresponding data from the cluster:
volumeMountPermissions:
var_run:
readOnly: true