These days, most organizations rely on a hybrid IT infrastructure and use the services of public cloud providers and their on-premises systems. Cloud infrastructure is more scalable and easier to adapt to your company's needs.
Nevertheless, you should continuously perform infrastructure monitoring, especially when migrating servers to the cloud environment and operating hybrid cloud environments.
What are cloud Servers?
These are technically virtual servers. Cloud services provide the functions of a server that operates as a virtual machine (VM) and enables the installation of applications.
A user can access these files on-demand through the internet, which means the underlying hardware platform is usually invisible to the user.
The physical basis and the management of the resources are the sole responsibility of the cloud operator.
The servers are usually purchased as a service from public cloud services providers such as AWS or Microsoft Azure or a private cloud provider.
Billing takes place based on various criteria, depending on the package booked, for example, according to the number and utilization of the CPU cores.
In particular, large cloud providers offer a wide range of services, categorized into three:
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), hosting servers, storage, and virtual computing services made available through the internet, e.g., Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Rackspace
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), which are scalable server computing power and complex application servers, e.g., Google Apps and Dropbox
- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), which are application development platforms that run on their own infrastructure. Examples include AWS Elastic Beanstalk and Red Hat OpenShift.
Cloud infrastructure monitoring is crucial
Very few organizations rely on purely cloud-based infrastructure. They usually continue to operate their network systems and on-premises servers but outsource individual services to the cloud. Therefore, it makes sense to monitor the provider's costs and service level agreements (SLAs) and keep an eye on the interaction of the various systems in their network. It is thus crucial that a monitoring tool enables the monitoring of such a hybrid environment. It ensures the maintenance of infrastructure health.
What is cloud server monitoring?
You should continuously monitor your systems to ensure their optimal application performance based on established custom metrics.
Most cloud providers collect monitoring data, making it available to monitoring tools via APIs. Use this information and put it in context with monitoring data from other systems.
The providers' onboard tools are usually of little help since they focus solely on their systems. However, contextual information is always crucial when monitoring the cloud.
Although the three cloud server categories need an application-based monitoring method, the environment in which each of these categories operates requires different approaches.
In an IaaS environment, you don't have to worry about the hardware, but you are in charge of installing and configuring the software. This means you are responsible for the best possible deployment of your applications.
With PaaS applications, for example, a development team deploys its apps on a platform supplied by a provider. The provider takes care of both the software and hardware, so the development team can focus on writing and managing their apps.
Users of SaaS applications lack visibility into the infrastructure. They depend on the limited data the SaaS provider shows through its APIs.
You need a monitoring solution
A monitoring tool optimized for a hybrid cloud infrastructure allows you to easily adapt to public or private clouds, on-premises infrastructure, or a combination of these resources and applications.
The ability to adapt makes things easier and allows you to gain a competitive advantage.
Additionally, with the correct monitoring tool, information once retrieved is available indefinitely, whereas providers usually only store it for limited periods.
If you use a solution from multiple providers, central monitoring of multi-cloud environments is also essential.
Therefore, a monitoring tool should be easily expandable to accommodate new providers and support standard providers such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
This way, you have all systems in one tool and don't have to switch between different monitoring interfaces. Maintaining optimum infrastructure health and performance thus becomes significantly easier.
Are cloud monitoring and cloud server monitoring the same thing?
No, they are not. Cloud server monitoring is one of the services under the broader cloud monitoring process.
Cloud Monitoring
Cloud monitoring observes, evaluates, and manages operational systems within a cloud-based infrastructure to ensure the health of cloud assets. These assets include apps, databases, storage, and more.
Regular cloud monitoring ensures the prevention of cloud-related issues. This approach may be applied to PaaS and SaaS, in which a third party provides the infrastructure.
Cloud Server Monitoring
Cloud server monitoring is a process for checking servers running in a cloud - database servers, file servers, web servers, Linux or Windows servers. However, cloud server monitoring is limited to the IaaS model, as it allows you to manage the underlying hardware in addition to the virtual servers. As a result, you are able to roll out the necessary monitoring agents to get a complete overview of your virtual servers, network, business processes and various other assets.
What can be monitored on cloud servers?
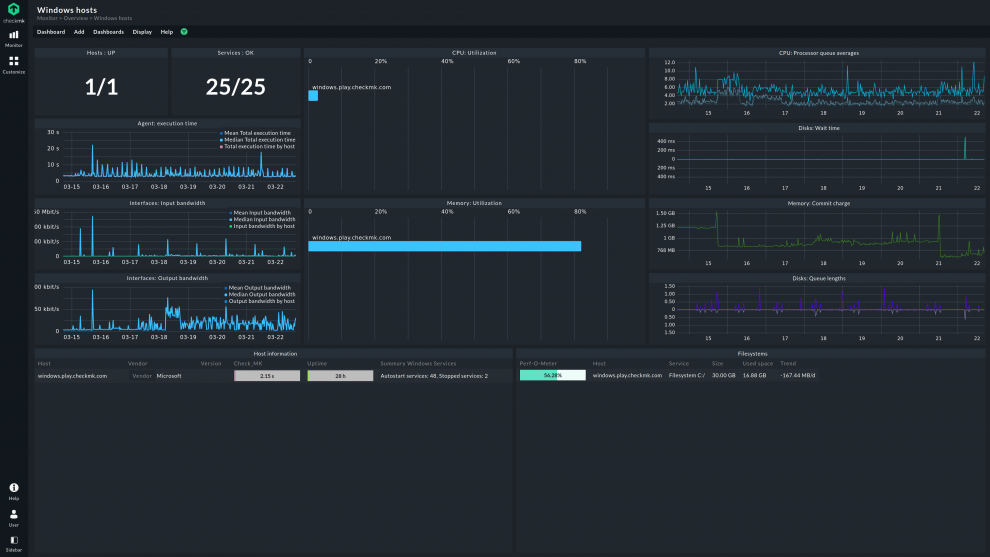
Everything monitored on a virtual server can be monitored on cloud servers: databases, virtual networks, and cloud storage. Install an agent software to access all data from the server.
Cloud servers show network connectivity status, hardware status, and API calls (data communications within the server).
Maintaining an operational status on network connectivity, hardware, and API ensures that your systems are at 100%.
Cloud server monitoring can also reveal other performance metrics such as error rates and response times.
Using the appropriate cloud monitoring services, e.g., Microsoft Cloud Monitoring, would help you pinpoint where the data breach or leak happened.
Why should I monitor cloud servers?
Cloud server tracking allows you to scale up your resources during peak usage or down during slack times. It enables you to focus on other critical business drivers.
With businesses becoming more reliant on technology, cloud servers boost overall operations and productivity. They make it possible for any team to work remotely and for employees to exchange data in real-time.
But what happens if the service is suddenly interrupted?
The most obvious effect is stopping your work for a few minutes or hours, but it can easily escalate into devastating losses.
You would want to run your servers in the cloud the right way and make them work as they should. Monitoring gives you the insights you need to do that.
With effective cloud monitoring, you can detect interruptions, be notified of server outages, and identify the problem immediately.
Solutions for easy monitoring
Cloud server monitoring is similar to virtual server tracking in that it gives you insights into your infrastructure's health. The insights gleaned through monitoring tools enable integrations for cloud monitoring.
A monitoring solution that supports API allows cloud providers to display data through their APIs. However, the data provided can be limited.
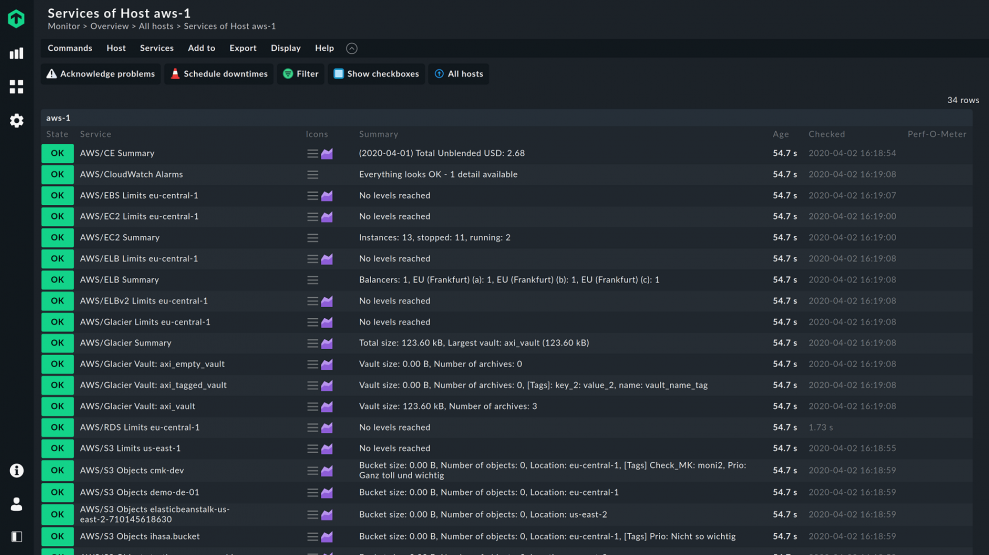
Checkmk has several integrations for AWS and Microsoft Azure. For example, with Microsoft Azure, you can register Checkmk as an app and configure it in minutes.
You thus have all nodes and servers from your cloud environment in an easy-to-understand host-service structure.
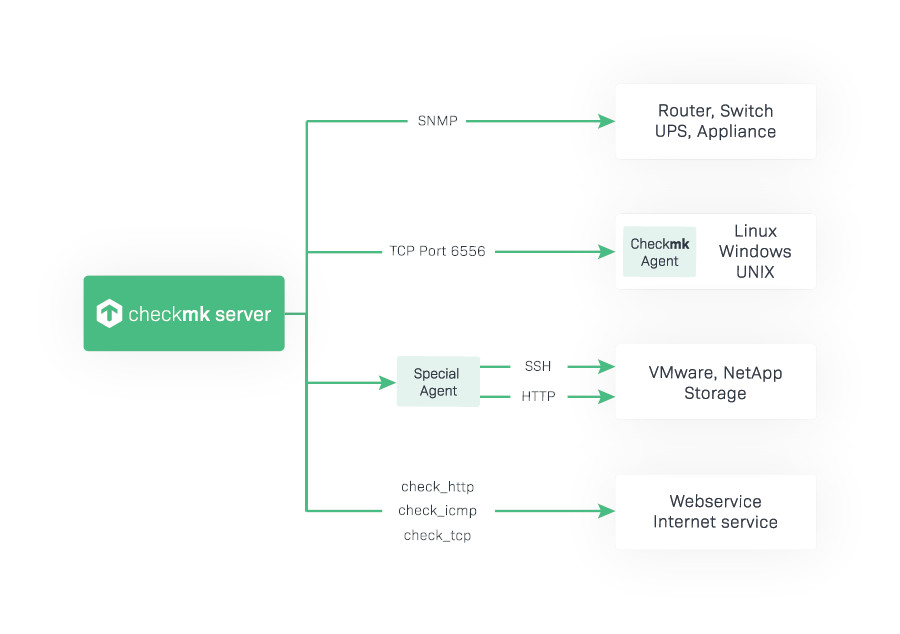
For monitoring, you only need to install a special agent on your local monitoring instance and activate access to the cloud provider.
The architecture of the Checkmk special agents is designed for flexible expansion and is continually being developed to extend its range of supported cloud monitoring packages.
Cloud applications features make monitoring easy
In addition to the agents and plug-ins explicitly designed for AWS and Microsoft Azure, Checkmk comes with many sophisticated features to make cloud monitoring easy.
Like monitoring virtual server environments, you can automate host management with the Dynamic Configuration Daemon (DCD).
For example, when monitoring Microsoft Azure, you can match the query intervals to Microsoft's rate limit not to exceed the allowable data queries limit.
With AWS, you can also precisely adjust the questions not to burden your systems budget unnecessarily.