What is AWS cloud monitoring?
AWS monitoring is about observing AWS-native solutions, resources, and services, hosted on the AWS cloud. Monitoring these means being able to collect, aggregate, and analyze metrics that inform administrators and cloud architects on the health and performance of applications running on the AWS platform. AWS monitoring is the part of the broader cloud monitoring that focuses on monitoring AWS environments.
As a public cloud service, Amazon Web Services (AWS) is vast and includes dozens of usage cases, making it a complex cloud infrastructure to manage. Therefore, AWS monitoring can become a quite complex task for IT administrators, depending on how many services are used and how they interact with each other. Monitoring and observability are crucial for gaining visibility into AWS cloud infrastructure, ensuring excellent performance, and proactively identifying issues.
AWS cloud offers a large range of services for companies that want their IT infrastructure to be performant and easily scalable. Databases, storage, virtual networks, computing environments, load balancers, virtual machines and much more can be hosted on the AWS cloud. These cloud services are suitable to host your IT infrastructure exclusively or to create a hybrid setup together with a local infrastructure. AWS monitoring is thus not isolated from local monitoring efforts, and often a single monitoring solution is implemented to monitor it all.
Given the breadth of AWS offerings, it is useful to examine the specific areas of the platform and understand what can be done and how it can be monitored. At the same time, effective AWS cloud monitoring requires defining clear objectives by identifying critical metrics, KPIs, and resources to prioritize monitoring activities.
What areas need to be monitored on an AWS cloud?
AWS environments consist of multiple domains, each serving different resource and computational needs. To ensure comprehensive monitoring, it is essential to develop a monitoring plan and define clear objectives for your AWS infrastructure. Depending on the services you are using, only certain areas may require active monitoring. For example, serverless applications or microservices will likely require a dedicated AWS compute monitoring strategy, whereas storage monitoring will focus primarily on AWS S3, the platform’s storage service. Or, if you are using a load balancer, AWS load balancing monitoring is another area to look into. It largely depends on how you use AWS services in practice, and whether you operate private data centers, hybrid setups, or multi-cloud environments that require monitoring solutions capable of handling diverse platforms.
AWS performance monitoring and AWS security monitoring are broader areas that influence all of AWS cloud services and resources. Following best practices for AWS monitoring is essential, as these areas need to be the focus of any AWS monitoring tool, impacting every type of AWS infrastructure setup and providing visibility across the entire organization.
At a bare minimum, AWS application performance monitoring is to be implemented on any cloud environment. Along with general performance and security monitoring, utilizing a full stack observability platform will ensure that AWS applications are optimally running and provide comprehensive insights for your monitoring needs.
AWS performance monitoring
Performance is always a key area to monitor. AWS clouds have lots of parts that influence the overall performance of an application, and therefore more than one tool exists for AWS performance monitoring. AWS itself comes with a few tools for application performance monitoring. Trace data, for example, is provided by AWS X-Ray. It tracks the execution of an application and reports a large set of technical information on it for debugging purposes. AWS Config provides an inventory of all configuration of the AWS resources. It is a helpful tool not only for its primary purpose, identifying misconfigurations, but noticing how configuration changes may impact performances.
AWS performance monitoring is mainly about checking the real-time metrics provided by AWS on its resources. EC2 instances, RDS databases, S3 buckets and others have individual signals for how well they are working. Key metrics to monitor include CPU utilization, memory usage, disk usage, and network performance, as these are essential for assessing system health and identifying potential issues. The main AWS tool to monitor these metrics is AWS Cloudwatch, which we will address later when talking about AWS service monitoring. For small applications and workloads, Cloudwatch has a clear-cut dashboard that can help administrators identify performance bottlenecks on their AWS cloud. For more complicated tasks, a dedicated AWS monitoring tool that provides a greater deal of customization and collectable metrics, including the ability to track custom metrics, is often more preferable.
AWS performance monitoring is as much about AWS application performance monitoring as resource monitoring. Both need to be checked to have a complete view of how your AWS environment is performing. Performance optimization plays a crucial role in ensuring that AWS resources and applications run efficiently and reliably.
AWS network monitoring
In both, full cloud and hybrid infrastructures, there is always more than one network operating at all times. The networks can span multiple datacenters, both private or public, and possibly increase packets’ latency. Even though AWS clouds are greatly optimized to reduce network issues, it is still essential to implement AWS network monitoring.
It is especially vital to be able to monitor both on-premises and cloud networks. Nowadays, it is rare to use only one exclusively, so your monitoring solution has to be able to monitor both to avoid an inconsistent monitoring and management experience. AWS has a few integrated tools that are helpful to get a view of your AWS networks. AWS Transit Gateway Network Manager can monitor your cloud networks as well as your on-premises ones. It can respond to connectivity problems and has a unified interface to identify any issues with a single glance.
To access the actual metrics related to AWS networks, a good starting point is monitoring the various Elastic Network Interfaces (ENI). These are virtual network cards in a VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) on AWS, exposing basic characteristics of a real network card, such as IP addresses – both public and private –, Mac address, security groups, source/destination flags, and a description. However, these are only basic information. To have a more holistic monitoring, you should definitely collect more metrics, for example through AWS APIs or by using a third-party AWS cloud monitoring solution. The effectiveness of your network monitoring depends on the quality and scope of the collected data, which should include logs, metrics, and traces from different sources.
Helpful are also network logs. Especially those of the VPCs and Load Balancers can give you a lot of insight into how, or if, an AWS network works. VPC Flow Logs are a key source of network data, allowing you to track and analyze data traffic in and out of your AWS environments. They are rather manual to check, thus a local monitoring solution that can export more metrics from AWS through a custom agent is highly preferable. Analyzing data from network logs and metrics helps you gain deeper insights into AWS network performance and quickly diagnose potential issues.
AWS security monitoring
Security is always an important factor to consider in any organization, and especially if a part of your IT infrastructure is delegated to a third-party service. Therefore, it is vital to be able to monitor the security of AWS monitoring. AWS itself has a handful of tools that can help with AWS security monitoring. These AWS security services, such as GuardDuty and Inspector, provide centralized security alerts, threat detection, and compliance enforcement.
AWS CloudTrail is the AWS service that can enable operational and risk auditing, compliance, and governance for the whole AWS account. It records a series of events that can be monitored in order to ensure that their resources and data were accessed by authorized actors only, helping you to identify and respond to unusual activity. CloudTrail works with Amazon GuardDuty, which is another AWS service that analyzes events from CloudTrail along with different types of logs to identify potentially malicious or unauthorized activity across the whole AWS account. Both are fundamental for basic AWS security monitoring. They can easily be replaced by third-party AWS cloud monitoring solutions, though.
AWS security monitoring is not only about identifying unauthorized accesses and events. It also includes preventing exploits of software from malicious external agents. AWS monitoring solutions can scan various AWS services to discover software vulnerabilities and unintended network exposure. For AWS clouds, Amazon’s Inspector tool performs this task. Similarly, AWS Config can assess and report on the configuration status and changes, easing troubleshooting and compliance audits.
All these tools are specific to AWS, and don’t really offer a unified view. Therefore, using a centralized cloud monitoring solution has the great advantage of visualizing the same or similar features in a single dashboard and reporting system. Implementing a custom dashboard allows you to organize, visualize, and prioritize security alerts and metrics from various AWS security services, tailoring the view to your specific monitoring needs. Security-related alerts play a crucial role in detecting and responding to threats in AWS environments, enabling teams to act quickly on suspicious activities and enforce compliance.
AWS Lambda monitoring
A pillar of serverless computing, AWS Lambda is one of the most commonly used AWS services, making AWS Lambda monitoring a necessity to ensure that the applications running on AWS are optimally performing, not under stress, and not possibly causing outages. AWS Lambda monitoring consists of controlling the usual metrics related to any application, like CPU usage, memory, disk, and network utilization.
Amazon offers Lambda Insights within the broader AWS CloudWatch service. Each Lambda application exports its key metrics to CloudWatch for analysis and troubleshooting as needed. These same metrics can be externally monitored through a monitoring software that supports AWS cloud monitoring.
Lambda applications have their own logs, which are also available to CloudWatch. As is clear by now, these logs are exportable and possible to view with an external AWS monitoring solution as well. AWS Lambda abstracts away the underlying infrastructure, making comprehensive monitoring even more important to maintain application performance and reliability.
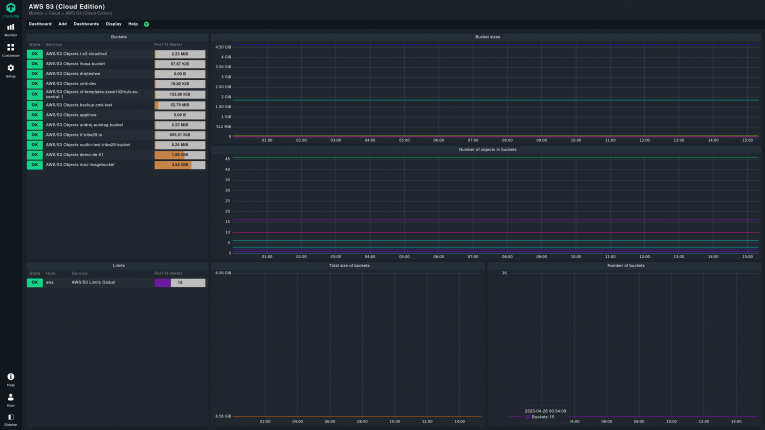
AWS S3 monitoring
AWS S3 (short for Simple Storage Service) is the AWS cloud service for data storage. This does not only include data for applications, but also backups and long-term storage of documents. These data can be hosted on various locations and with different tier usages, depending on their level of desired availability.
Ensuring that S3 data is safe and untouched is the task of AWS S3 monitoring. It naturally overlaps with AWS security monitoring, since data is a part of the overall resources of an infrastructure, and needs to be secured from external parties. To guarantee that data is not lost or tampered with, AWS offers a few possibilities. The first option is the S3 Access Analyzer that alerts about S3 buckets (a virtual container for objects stored on S3) which are publicly available on the internet or outside your organization. For each bucket, information about the level of access and its source are provided. Misconfigured file permissions against an access policy are also reported.
Along with the usual availability of logs, it is possible to have a good idea of what files have been accessed, by whom, when, and if changes were made.
To enable actual security of the data, Amazon includes the S3 Inventory tool. It is used to audit and report on the replication and encryption status of your objects. In this regard, AWS S3 monitoring is basically a branch of the broader AWS security monitoring.
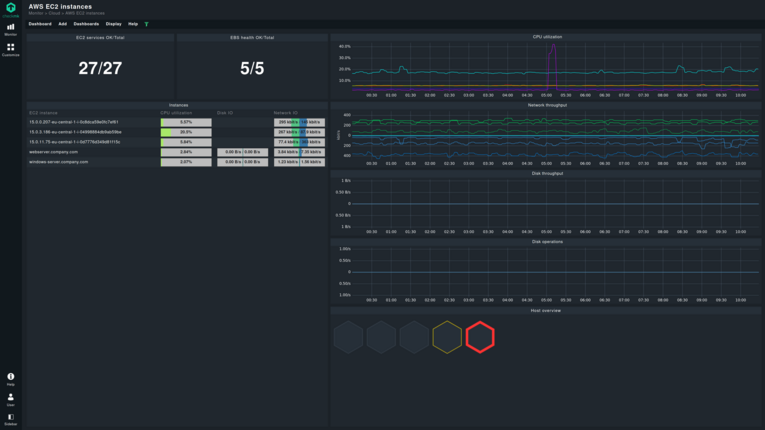
AWS EC2 monitoring
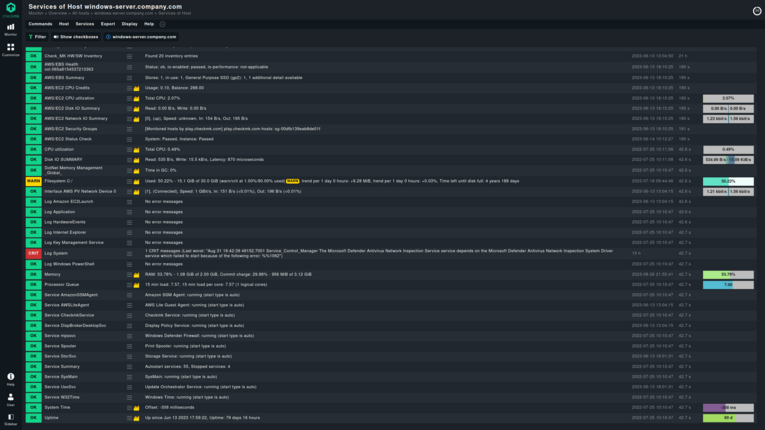
For cloud workloads, and for basically having a virtual server available for your computational needs, AWS comes with EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud). Many applications are run on EC2 instances, making AWS EC2 monitoring an important aspect of AWS monitoring. Unsurprisingly, by now, both Amazon and third-party solutions can monitor EC2 to check on your virtual servers and detect any problems.
AWS provides some metrics to inform about the health of EC2 instances. These metrics include CPU, network, and disk utilization, as well as disk-specific performance metrics such as overall reads/writes, disk space, page file, and swap utilization, along with memory usage. They are all necessary in order to knowif your applications have enough resources to operate. Monitoring tools not only track these metrics but also help identify the root cause or root causes of performance problems or outages, enabling faster troubleshooting and more effective prevention of future incidents.
AWS CloudWatchalso includes AWS EC2 monitoring and combines the metrics mentioned above in its dashboard. Similarly, plenty of other cloud monitoring systems, such as Checkmk, collect these metrics as well, and offer you a holistic view of your whole infrastructure no matter where it is located.
AWS RDS monitoring
Databases are part of every infrastructure, and an AWS cloud is no exception. As the repository for key operational data, database monitoring is naturally an important part of any company’s monitoring efforts. On AWS, the RDS (Relational Database Service) supports a vast choice of databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, Oracle and SQL Server) to fit any need.
AWS RDS monitoring is the branch of AWS monitoring that takes care of monitoring all types of databases. AWS collects a series of key metrics to inform you on how well the databases are performing. The main ones are number of connections, amount of read and write operations, amount of storage, memory and CPU used by each database, and network traffic directed to the database. As with other AWS services, RDS logs are available to use for further insights and analysis when monitoring your AWS databases.
All these metrics and logs are available to CloudWatch and to the more specific Amazon RDS Performance Insight tools. External agents, like those used by Checkmk, can collect both metrics and logs to work with complete cloud monitoring solutions without relying on Amazon’s proprietary tools.
AWS load balancing monitoring
Load balancers are services that automatically distribute incoming traffic across multiple targets. For instance, EC2 instances, containers, API Gateway, and a set of IP addresses can be put behind a load balancer to distribute requests. Every time a new request comes in, the load balancer takes care to compute what of the resources it manages is more free and can thus take charge of the request. A load balancer is a key element of cloud scalability, and naturally AWS has its one.
In multi tiered applications, monitoring load balancers is crucial to ensure reliable connectivity and good performance across all layers of the architecture.
On AWS, the load balancer is called Elastic Load Balancer, and is the component that needs to be monitored when doing AWS load balancing monitoring. It may only be a small part of an infrastructure, but an extremely important one nonetheless. If the load balancer fails or misbehaves, some resources would see a large increase in workloads, while other resources are left to idle.
AWS Elastic Load Balancer exposes, to CloudWatch and externally, metrics such as the total number of TCP connections active from clients, the number of non-compliant network requests, the number of redirects, the number of targets that are healthy (thus considered open to accept requests), and many more. Along with its logs, AWS load balancing monitoring can easily be done with either CloudWatch or an external cloud monitoring tool.
Monitoring AWS resources and costs
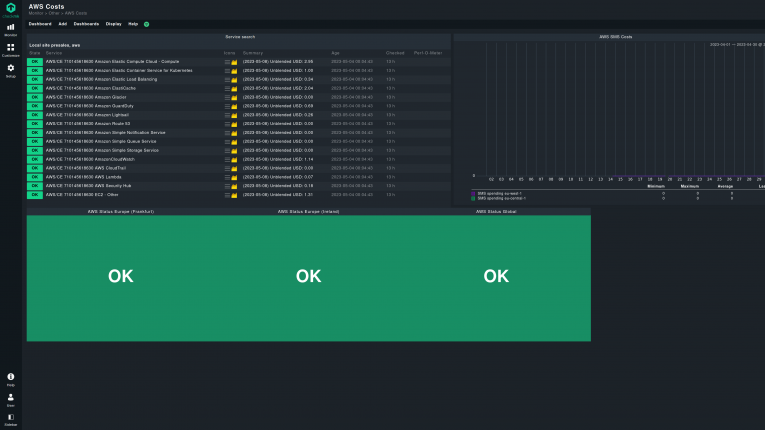
The last area to monitor is AWS global resource usage and its relative impact on costs. Any cloud service comes with costs that need to be budgeted. The resource usage is directly related to cost, with some free tiers available before fees become mandatory. A good part of AWS observability is collecting data from your AWS environment that include insights into both resource usage and associated costs.
AWS offers some tools to keep the costs under control. AWS Cost Explorer, once enabled, creates 24 hours reports on the current and forecasted costs for your AWS cloud service utilization. It is part of the broader AWS Billing and Cost management service, which includes usage reports. Third-party AWS monitoring tools support checking your cost and resource utilization on AWS, and are usually a better choice since their reports are more complete and contain customizable monitoring dashboards for visualizing AWS costs.
In case budgeting is needed to better plan your AWS cloud usage, AWS Budgets is another service from Amazon that helps you set up yours, and alerts you when you went over budget and where. These alerts are triggered based on predefined thresholds, allowing you to respond quickly when spending exceeds your set limits. If that happens, there is yet another tool that can help you identify the cause of surpassing your intended expenditures on AWS cloud, AWS Cost Anomaly Detection. It is a monitoring system just for AWS costs that can analyze seasonal and past usage patterns, set thresholds, and send alerts for identifying the cause of overspending.
For organizations managing multiple AWS accounts, AWS Organizations enables centralized monitoring and management, simplifying multi-account setups and providing unified visibility across your cloud environment.
Automating continuous monitoring of AWS costs and resources helps ensure ongoing oversight, improves efficiency, and reduces the risk of unexpected expenses.
Choosing the right AWS monitoring tool
Selecting the right AWS monitoring tool is a foundational step in achieving performance, security, and cost optimization for your AWS environment. With a wide array of AWS monitoring tools available, it’s important to assess your organization’s unique needs before making a decision. Start by considering the specific AWS services you rely on and the complexity of your AWS infrastructure. The best monitoring tools offer seamless integration with multiple AWS services, ensuring you have complete visibility across your entire AWS cloud.
Look for a monitoring tool that provides real-time monitoring, customizable dashboards, and robust visualization options to help you rapidly identify and troubleshoot issues related to performance. Scalability is also key — your monitoring solution should grow with your AWS environment and adapt to changing requirements. Automated monitoring features, such as predefined alerts and recommended monitors, can help you stay proactive and address issues before they impact your operations.
By choosing the best AWS monitoring tool for your use case, you give your team the means to maintain optimal performance, reduce AWS cloud costs, and ensure your AWS infrastructure is always running smoothly. Complete visibility and actionable insights are essential for making informed decisions and keeping your AWS environment secure and efficient.
Monitoring with AWS CloudWatch
AWS CloudWatch stands out as a powerful native AWS monitoring service, designed to provide real-time monitoring and troubleshooting for your AWS resources and applications. With AWS CloudWatch, you can collect, track, and analyze metrics, logs, and events from a wide range of AWS services, including Amazon EC2, Amazon S3, and Amazon RDS. This monitoring service offers customizable dashboards and alarms, allowing you to visualize system performance and quickly identify performance issues as they arise.
CloudWatch enables you to monitor critical aspects such as API calls, network traffic, and resource usage, giving you end-to-end visibility into your AWS environment. Its seamless integration with other AWS services, like AWS CloudTrail and AWS Config, ensures a comprehensive monitoring solution for your AWS infrastructure. By leveraging AWS CloudWatch, you can stay ahead of potential problems, optimize your AWS resources, and maintain the health and performance of your AWS cloud.
Using AWS CloudTrail
AWS CloudTrail is an essential AWS monitoring tool that provides detailed visibility into API calls and user activity across your AWS infrastructure. By recording every action taken on your AWS resources, CloudTrail creates a comprehensive, searchable log of events, making it easier to track changes, monitor security events, and detect suspicious activity.
CloudTrail’s integration with AWS CloudWatch allows you to monitor and analyze log data in real time, helping you identify performance degradation and optimize resource utilization. This monitoring tool is invaluable for maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements and improving the overall security posture of your AWS environment. With a complete history of API calls at your fingertips, you can troubleshoot issues efficiently and ensure your AWS resources are being used effectively.
Real-time, automated monitoring
By using AWS monitoring tools such as CloudWatch and CloudTrail, you gain continuous visibility into your AWS resources, allowing performance issues and security threats to be detected and addressed quickly. These tools provide real-time, automated monitoring, forming an essential part of a comprehensive AWS monitoring approach.
Automated monitoring should analyze logs, metrics, and events from your AWS infrastructure, providing actionable insights that help you optimize resource usage and reduce costs. With real-time alerts and continuous monitoring, you can quickly identify and resolve issues before they impact your applications or customer satisfaction. Implementing automated monitoring not only supports optimal performance but also streamlines operations, allowing your team to focus on innovation rather than manual oversight.
Monitoring AWS environment and beyond
AWS’s native monitoring services are primarily designed for AWS environments. For example, while CloudWatch can partially monitor on-premises resources, it does not support other cloud providers such as GCP or Azure. For smaller setups, these tools may be sufficient. But as infrastructure grows or requires greater flexibility, an external monitoring solution becomes essential. Third-party tools can be deployed on AWS or from local servers, enabling monitoring of a wide range of AWS services while integrating data from on-premises systems and other clouds into a unified view.
Checkmk is one such tool. It can be installed locally or via the AWS Marketplace, collecting metrics through AWS APIs or monitoring agents installed within the AWS environment.
A unified monitoring tool simplifies managing large infrastructures by aggregating metrics from diverse sources, including multiple cloud providers — critical since most environments now rely on more than one cloud.
Why it is important to monitor an AWS cloud
An AWS cloud is a complex ecosystem made of thousands of services and resources. It is easy for any of them to go awry and cause issues to the others. Outages, reduced performances, and increased costs are only a small part of what a misconfigured or malfunctioning AWS service may cause.
AWS monitoring solutions aim to prevent all this, or, in the worst case, give the IT administrators enough information to understand what went wrong and how to fix it. Either way, without an AWS cloud monitoring system in place, none of the above would be possible.
AWS recognized the need for monitoring their cloud platform and now offers multiple tools for this task. There are also plenty of third-party solutions that can give you greater insights in what your AWS cloud is doing and how. Checkmk is only one example among many.
Whatever solution you choose for your cloud, monitoring AWS services, performance, security, and resources is vital to ensure that it works smoothly, and to prevent outages. The amount of data that is exchanged and hosted on an AWS cloud is large and important enough to warrant setting up an AWS cloud monitoring solution. Simple or advanced, not monitoring such a vital part of your IT infrastructure is like welcoming a disaster.
In modern infrastructure, cloud services are a key element. Monitoring them is therefore a key task for any IT administrator that has to manage a hybrid or fully cloud-based environment.
FAQ
What is AWS SNS?
AWS SNS is a service for AWS clouds to set up and send notifications from the cloud. It allows administrators to send notifications through SMS messages or mobile push notifications, informing users or administrators of events related to their AWS cloud services or account.