Network Flow Monitoring: Analyzing your network traffic
From Checkmk 2.0 onwards, it will be possible to gain deeper insights into your network thanks to the deep integration of ntop's network flow monitoring in the Checkmk Enterprise Edition. By integrating ntop's analysis of flow packets, it is possible to see in-depth and relevant information from the network traffic in Checkmk. The administrator can thus learn who is doing what, when and where in the network and in this way identify possible bottlenecks or anomalies in his network environment.
The insights into network traffic obtained via flow monitoring go even deeper than the data on bandwidth, status or the utilization of network components obtained through an SNMP query, for example.
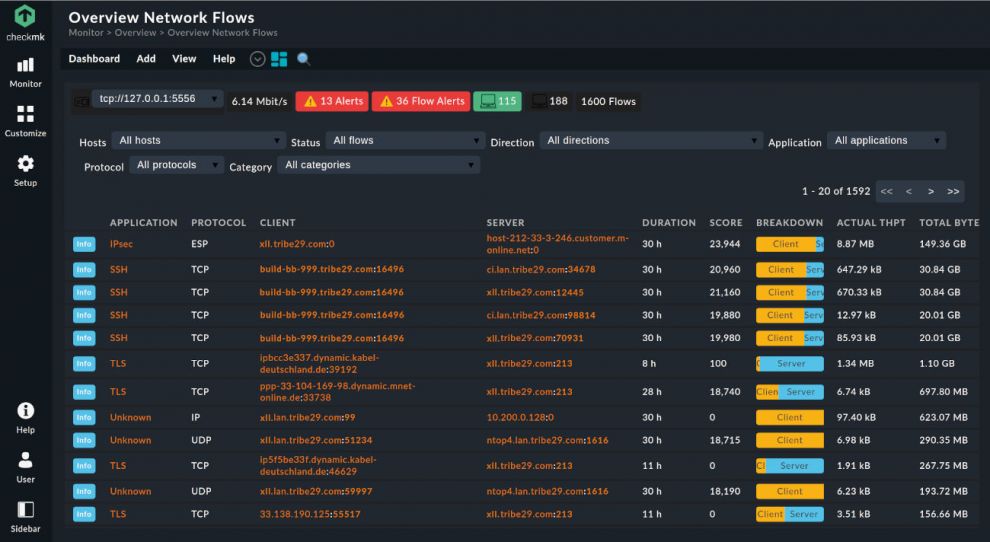
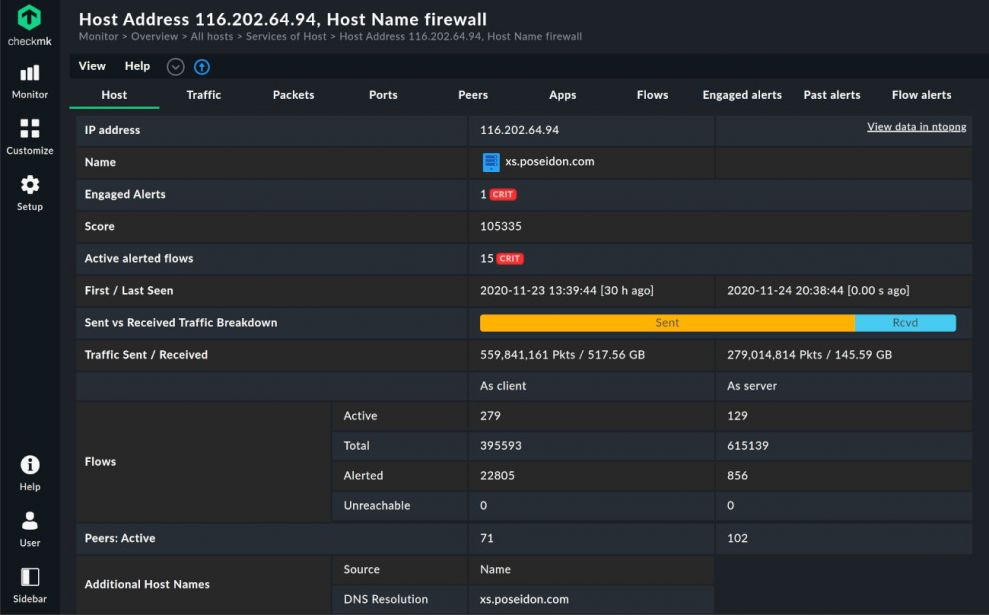
Checkmk 2.0 makes it possible to view ntop's visualised flow data in Checkmk. The deep integration of ntop's network flow monitoring in Checkmk provides you with information about the network details of your hosts, among other things. In addition to basic information of a specific host, the integration provides you with insights into traffic, packets, ports, peers, applications and flows. A flow dashboard gives you an overview of the data flows in your network. All this information can be accessed and viewed from the ntop servers via Checkmk's monitoring interface.
Simplified configuration for switch port monitoring
The ntop integration is not the only innovation that Checkmk 2.0 has in store for network monitoring. With the new version we also wanted to simplify the configuration of network monitoring.
For this purpose, we have revised the discovery rules for network interfaces and switch ports. Before version 2.0, Checkmk separated the discovery of individual network interfaces from the discovery of grouped interfaces. The user thus had to coordinate both sets of rules in order to be able to detect grouped interfaces. Checkmk 2.0 now combines this in the standard rule set for the detection of network interfaces. Overlapping rules are thus now possible.
The ruleset for discovering network interfaces has been thus also completely reworked to make it more easier to use and is now separated into three parts:
- What kind of service does the user want to create? (grouped/individual?)
- What parameters does the user want to apply to the discovered service, for instance, setting an index or alias in the service name?
- Which interfaces should Checkmk take into account for a discovery?
With this we have aimed to significantly simplify the workflow. We have also separated the setting for the admin states from the other states, as this is a rare use case.
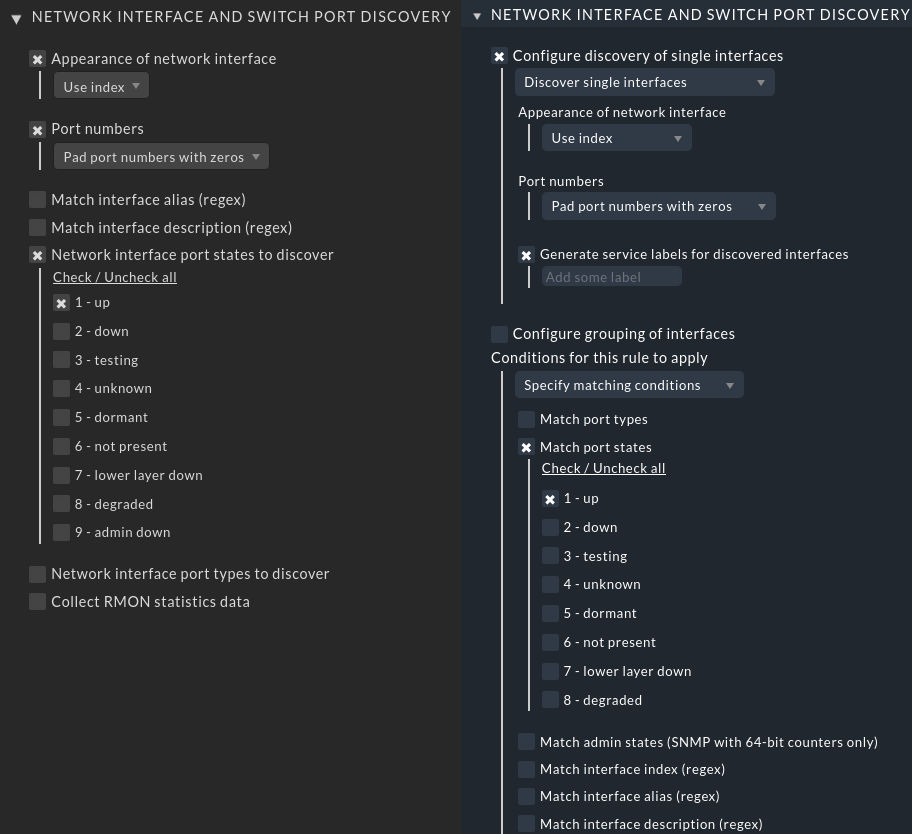
For most users, no migration will be needed. However, if you for example used the ruleset for grouping interfaces or configured the discovery of 'admin states', then a migration for sure will be required.
More information about Checkmk 2.0
For deeper insights into the many changes and features Checkmk 2.0 has in store, read one of our blog posts on a specific topic:
- More modern, intuitive and individual – the new UX
- Clouds and containers – monitoring of modern IT assets
- New APIs provide automation and more stability
- More power under the hood - improvements to the Checkmk core
- A broad foundation for your IT monitoring
You can also find more information about Checkmk 2.0 in the Checkmk forum in our documentation or on our YouTube channel.